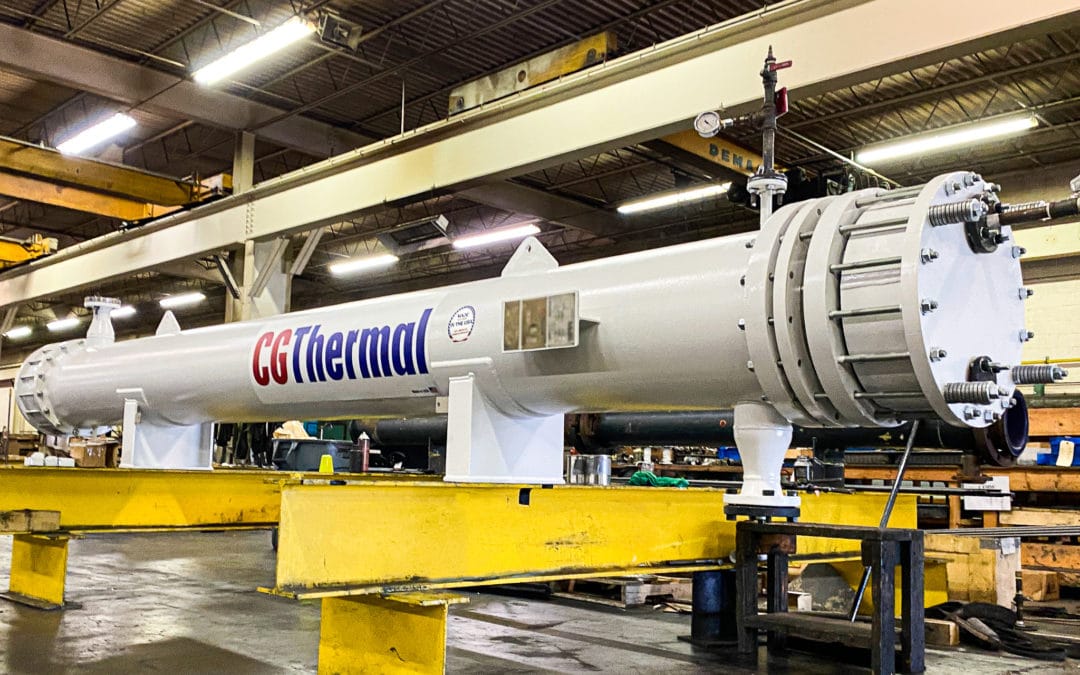
There are many applications for graphite, and it has long been a sought-after heat transfer material for harsh and corrosive process streams. It is particularly useful because it exhibits both metallic and non-metallic properties that contribute to equipment longevity and reliability.
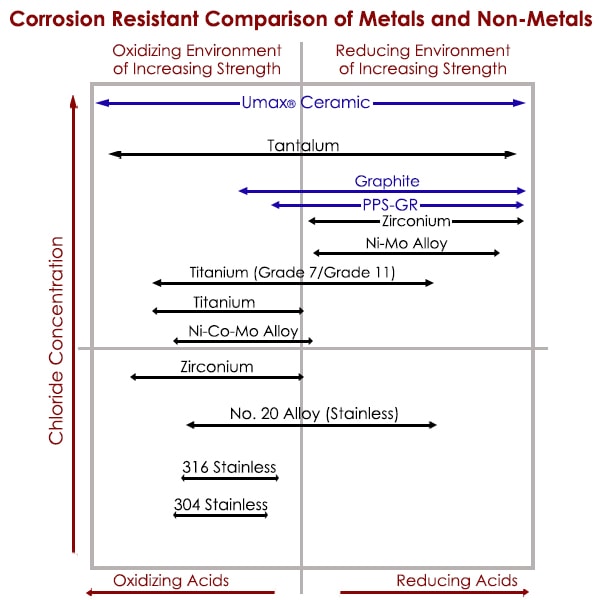
Along with high thermal conductivity, graphite also has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity (CTE), similar to or better than that found in metals. Additionally, graphite is inert, making it exceptionally resistant to corrosion. In total these properties make graphite an ideal heat transfer media for many highly corrosive processes.
Since graphite is very stable in highly reducing environments, it is widely considered as the economical and value-added choice for processes involving hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, and methyl chloride. Because of this, it is especially effective at elevated temperatures and higher concentrations which exceed the capabilities of most metallic materials.
Graphite can also be an appropriate choice for mildly oxidizing process applications. For instance, it can be used with sulfuric acid at concentrations as high as 70% when first cost is the driving factor. However, in a highly oxidizing environments, graphite will react to form carbon dioxide and result in material failure.
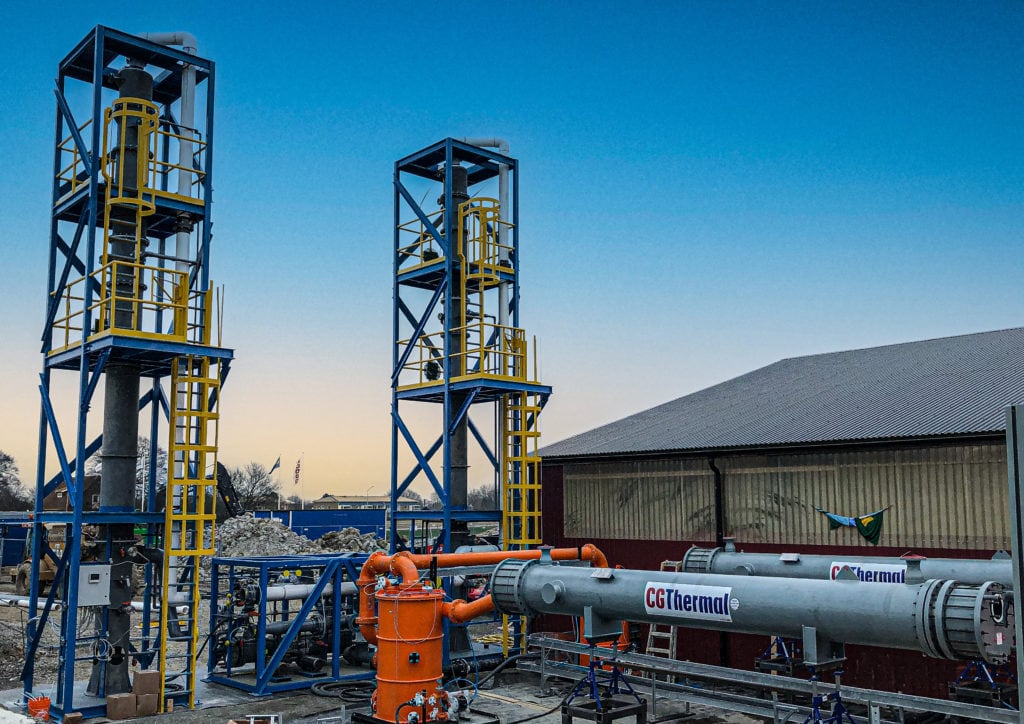

Industries where graphite heat exchangers are common include fertilizer, agro-chem, VCM, plastics, environmental remediation, specialty chemical, and more.
CG Thermal, Experts in Highly Corrosive Process System Design and Graphite Application
Equipped with more than 150 years of combined experience, CG Thermal designs and manufactures industry-leading Impervite® graphite heat exchangers. We also design the turnkey systems that may require graphite heat exchangers.
Want to learn more about quality impervious graphite and why it makes a difference? Download CG Thermal’s white paper to learn more. Our paper details the characteristics of resilient and long-lasting graphite, code standards, and the graphite impregnation process.